What is SPF, how does it work and what parts does it consist of?
SPF is short for Sender Policy Framework (formerly Sender Permitted From).
SPF determines whether or not a sender is permitted to send on behalf of a domain. If the sender is not permitted to do so, that is, if the email fails the SPF check on the receiving server, the spam policy configured on that server determines what to do with the message.
Each SPF TXT record contains four parts:
- the declaration that it is an SPF TXT record
- the IP addresses that are allowed to send mail from your domain
- and the external domains that can send on your domain's behalf
- and an enforcement rule
You need all in a valid SPF TXT record. .
How to set an SPF entry for Office 365:
On your hosting provider's website, edit the existing SPF record or create an SPF record. Make sure that the fields are set to the following values:
- Record Type:
TXT (Text) - Host:
@ - TXT Value:
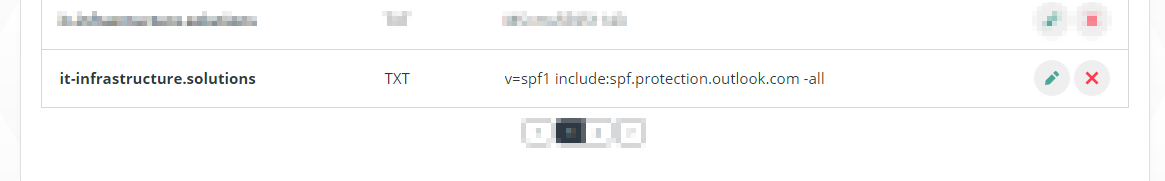
v=spf1 include:spf.protection.outlook.com -all - TTL:
3600(or your provider default)
Save the record.
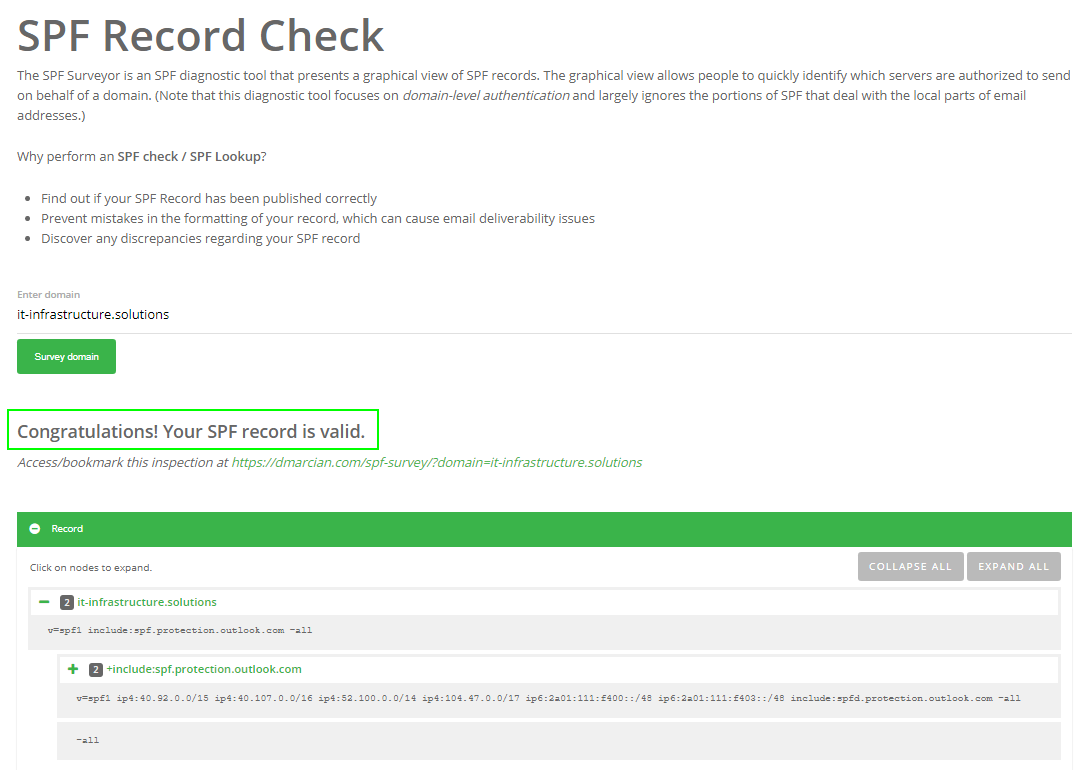
For my domain "it-infrastructure.solutions" the whole thing looks like this:
How to check if everything works as expectet:
Validate your SPF record by using one of these SPF validation tools
SPF is designed to help prevent spoofing, but there are spoofing techniques that SPF cannot protect against. To protect against these, once you've set up SPF, you should also set up DKIM and DMARC for Microsoft 365.
However, at the moment I will stop here (I would like to discuss this in another blogg post later on.)


